Definition of Fock space
Fock space is the (Hilbert) direct sum of tensor products of copies of a single-particle Hilbert space 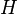
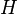
Here 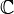 , a complex scalar, represents the states of no particles,
, a complex scalar, represents the states of no particles, 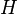 the state of one particle,
the state of one particle,  the states of two identical particles etc.
the states of two identical particles etc.
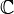 , a complex scalar, represents the states of no particles,
, a complex scalar, represents the states of no particles, 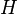 the state of one particle,
the state of one particle,  the states of two identical particles etc.
the states of two identical particles etc.
A typical state in  is given by
is given by
 is given by
is given by
where
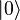 is a vector of length 1, called the vacuum state and
is a vector of length 1, called the vacuum state and  is a complex coefficient,
is a complex coefficient, is a state in the single particle Hilbert space,
is a state in the single particle Hilbert space, , and
, and  is a complex coefficient
is a complex coefficient- etc.
The convergence of this infinite sum is important if  is to be a Hilbert space. Technically we require
is to be a Hilbert space. Technically we require  to be the Hilbert space completion of the algebraic direct sum. It consists of all infinite tuples
to be the Hilbert space completion of the algebraic direct sum. It consists of all infinite tuples  such that the norm, defined by the inner product is finite
such that the norm, defined by the inner product is finite
 is to be a Hilbert space. Technically we require
is to be a Hilbert space. Technically we require  to be the Hilbert space completion of the algebraic direct sum. It consists of all infinite tuples
to be the Hilbert space completion of the algebraic direct sum. It consists of all infinite tuples  such that the norm, defined by the inner product is finite
such that the norm, defined by the inner product is finite
where the  particle norm is defined by
particle norm is defined by
 particle norm is defined by
particle norm is defined by
i.e. the restriction of the norm on the tensor product 

For two states
 , and
, and
the inner product on  is then defined as
is then defined as
 is then defined as
is then defined as
where we use the inner products on each of the  -particle Hilbert spaces. Note that, in particular the
-particle Hilbert spaces. Note that, in particular the  particle subspaces are orthogonal for different
particle subspaces are orthogonal for different  .
.
 -particle Hilbert spaces. Note that, in particular the
-particle Hilbert spaces. Note that, in particular the  particle subspaces are orthogonal for different
particle subspaces are orthogonal for different  .
.



No comments:
Post a Comment